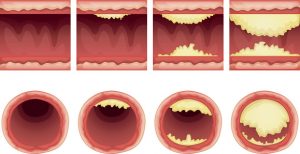
-
Gallery of Images:
-
More significant, perhaps, is the potential of functional foods to mitigate disease, promote health, and reduce health care costs. Functional Foods From Plant Sources Overwhelming evidence from epidemiological, in vivo, in vitro, and clinical trial data indicates that a plantbased diet can reduce the risk of chronic disease, particularly cancer. Functional foods are foods that have health benefits beyond normal nutrition. Functional foods range from cereals and bars enriched with folic acid to your average tomato or cup of green tea, while nutraceuticals are more commonly sold in pill form. Health benefits of functional foods There are many heath benefits that are linked to the superfoods that are regarded as functional foods. In Eastern cultures these superfoods are part of the everyday healthy diet and considered to have medicinal and therapeutic value. The Functional Foods in Health and Disease (FFHD) journal is a peerreviewed open access journal. Our journal discusses various aspects of functional foods, bioactive compounds, and chronic diseases. The FFHD journal develops research to better understand the mechanisms of disease and support the development of functional foods. Functional foods may be designed to have physiological benefits andor reduce the risk of chronic disease beyond basic nutritional functions, and may be similar in appearance to conventional food and consumed as part of a regular diet. More significant, perhaps, is the potential of functional foods to mitigate disease, promote health, and reduce health care costs. Overwhelming evidence from epidemiological, in vivo, in vitro, and clinical trial data indicates that a plantbased diet can reduce the risk of chronic disease, particularly cancer. Naturopathic medicine is an integrative, functional, and holistic form of medicine that emphasizes disease prevention and lifestyle modifications in an ordered and logical way. It aims to identify and remove the root cause of imbalances in the body, by addressing and treating the whole person. Functional foods and food components are being extensively studied for their effects as they relate to the optimization of human health and wellbeing, and in. Bioactive Compounds in Health and Disease. View Journal Current Issue Register. Functional Foods in Health and Disease. View Journal Current Issue Register Module Description: To provide a biochemical and physiological basis for the role of functional foods in health and disease and to give an overview of the strategies used in the development of functional food ingredients and bioassays used to examine the effect of such ingredients on health. Functional foods and nutraceuticals, dietary supplements, and natural antioxidants have established their potential roles in the protection of human health against disease. Functional foods are foods that provide health benefits beyond basic nutrition due to certain physiologically active components, which may or may not have been manipulated or modified to enhance their bioactivity. These foods may help prevent disease, reduce the risk of developing disease, or enhance health. The term functional foods refers to foods and their components that may provide a health benefit beyond basic nutrition. Functional foods do more than meet minimum daily nutrient requirementsthey also can play a role in reducing the. Functional foods are only one aspect of diet, and diet is only one aspect of a comprehensive lifestyle approach to good health, which should include regular exercise, tobacco avoidance, maintenance of a healthy body weight, stress reduction, and other positive health practices. Functional Foods in Health and Disease 2015; 5(6): Page 212 of 223 A nutrient content claim describes the actual components of a food product without any reference to health 1. Functional foods and nutraceuticals, dietary supplements, and natural antioxidants have established their potential roles in the protection of human health against disease. Nutraceuticals and Functional Foods in Human Health and Disease Prevention examines the benefits, efficacy, and success of. Functional Foods: Their role in disease prevention and health promotion A PUBLICATION OF Executive Director, Functional Foods for Health Program, University of Illinois, Dept. of Food Science and Human Nutrition, 103 ABL (MC 640), 1302 W. Magazine articles and news reports tout the benefits of eating functional foods, which they claim can do everything from reduce cholesterol to prevent conditions such as heart disease or cancer. Functional foods are foods that help you fight diseases and maintain your health besides providing essential nutrients. Examples include fruits and vegetables, whole grains, fortified produce and few dietary supplements. The Journal of Functional Foods aims to bring together the results of fundamental and applied research into healthy foods and biologically active food ingredients. The Journal is centered in the specific area at the boundaries among food technology, nutrition and health welcoming papers having a good functional foods. Functional foods can be defined as dietary items that, besides providing nutrients and energy, beneficially modulate one or more targeted functions in the body, by enhancing a certain physiological response andor by reducing the risk of disease (Nicoletti, 2012). Functional Food Center is pleased to announce its 21st International Conference and Expo on Functional Foods titled, Functional Foods and Bioactive Compounds in Health and Disease: Science and. The Journal of Functional Foods aims to bring together the results of fundamental and applied research into healthy foods and biologically active food ingredients. The Journal is centered in the specific area at the boundaries among food technology, nutrition and Functional foods, ageing and degenerative disease is a standard reference for all those concerned with the role of functional foods in the prevention and control of degenerative disease. Key Features Explores diet strategies for preventing diseases including osteoporosis Dubbed functional foods by experts, these foods promote optimal health by helping to reduce the risk of disease, boost your metabolism, aid with digestion, improve nutrient absorption, and help you lose weight, all while satisfying your hunger cravings. Optimize your diet with these foods and tips so you can look and feel your best self. A functional food is a food that provides benefits beyond basic nutrition. Functional foods play a role in reducing the risk of certain diseases or negative health conditions and can also increase the healing ability of the body and can provide specific health benefits. The Role of Functional Foods in the Psychobiology of Health and Disease Mark Hamer1, Gail Owen 2, Joris Kloek 2 1Department of Epidemiology Public Health, University College London, UK 2. These foods, also known as functional foods, are thought to provide benefits beyond basic nutrition and may play a role in reducing or minimizing the risk of certain diseases and other health conditions. Functional foods do more than simply meet nutritional needs, they have a tremendous impact on human health. In many cases their bioactive makeup can help ward off chronic diseases and other health risks. NutriWatch Home PageFunctional Foods: Their Role in Disease Prevention and Health Promotion A Publication of the Institute of Food T Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site. Functional Foods in Health and Disease's journalconference profile on Publons, with 12 reviews by 11 reviewers working with reviewers, publishers, institutions, and funding agencies to turn peer review into a measurable research output. For functional foods to deliver their potential public health benefits, consumers must have a clear understanding of, and a strong confidence level in, the scientific criteria that are used to document health effects and claims. Functional Foods, Health Benefits healthrelated costs of allowing disease risk reduction health claims on foods containing soluble fibre (specifically, barley and psyllium), as well as on soy protein. The growing burden of health care costs remains a key policy issue in Functional Foods in Health and Disease: 11: Page 447 of 456 was noted within 1016 days of regular administration of chlorophyll derivatives [12. It was reported that chlorophyll enhanced the formation of blood cells in anemic animals [13. The Journal of Functional Foods in Health and Disease (FFHD) 68 followers. Follow The Journal of Functional Foods in Health and Disease (FFHD) to stay uptodate with news, articles and jobs. While all foods are functional to an extent, the term implies a health benefit beyond the mere provision of calories or nutrients. One of the ways Functional Medicine seeks to address declining health is to provide the foods and nutrients needed to restore function. This is a cost effective, noninvasive intervention that aims to stop the progression into disease. Functional foods, ageing and degenerative disease is a standard reference for all those concerned with the role of functional foods in the prevention and control of degenerative disease. Show less Degenerative diseases linked to ageing populations are a growing problem for the developed world. The Functional Foods in Health and Disease (FFHD) journal is a peerreviewed open access journal that publish articles related to food and its relevance to health and disease. Open Journal Systems Managed Hosting; Open Journal Systems Installation and Setup . Functional foods are similar in appearance to conventional foods; the former being consumed as part of the normal diet. In contrast to conventional foods, functional foods, however, have demonstrated physiological benefits and can reduce the risk of chronic disease beyond basic nutritional functions, including maintenance of gut health [. Functional foods are foods that have a potentially positive effect on health beyond basic nutrition. Proponents of functional foods say they promote optimal health and help reduce the risk of disease. The Functional Foods in Health and Disease (FFHD) journal is a peerreviewed open access journal. Our journal discusses various aspects of functional foods, bioactive compounds, and chronic diseases. The FFHD journal develops research to better understand the mechanisms of disease and support the development of functional foods. Free radicals damage contributes to the etiology of many chronic health problems such as cardiovascular and inflammatory disease, cataract, and cancer. Antioxidants prevent free radical induced tissue damage by preventing the formation of radicals, scavenging them, or. Claims about the health benefits of functional foods should be based on sound scientific evidence, but too often only socalled emerging evidence is the basis for marketing some functional foods or their components. Functional foods: their role in disease prevention and health promotion. Functional foods and natural health products encompass a wide range of food and ingredients, with a variety of bioactives responsible for their efficacy in health promotion and disease prevention. Phenolic and polyphenolic compounds constitute an important class of secondary plant metabolites that act as free radical scavengers and inhibitors. The anticancer effects in various human and murine cancer cell lines have been shown in both in vitro and in vivo studies. The inhibiton of oral mucosa cancer by Ganoderma triterpene is due to. The Journal of Functional Foods in Health and Disease (FFHD) is a peerreviewed open access journal that covers various aspects of functional foods, bioactive compounds (Prebiotic compounds, Sterols, Minerals, Vitamins. Nutraceuticals, Functional Foods and Dietary Supplements in Health and Disease FEREIDOON SHAHIDI Department of Biochemistry, Memorial University of Newfoundland, St. Johns, NL, Canada While many definitions exist, Health Canada has stated that a functional food is, similar in appearance to, or may be, a conventional food, is consumed as part of a usual diet, and is demonstrated to have physiological benefits andor reduce the risk of chronic disease beyond basic nutritional functions. 1 Whereas, the American Dietetic.
-
Related Images: